What to Do to Get Heart Rhythm Normally Again
Overview
What is an arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia (also chosen dysrhythmia) is an irregular or aberrant heartbeat.
What is my pulse?
Your pulse indicates your heart rate, or the number of times your heart beats in one minute. Pulse rates vary from person to person. Your pulse is slower when you are at residue and increases when you exercise, since more oxygen- rich blood is needed past the body during exercise.
How do I have my pulse?
You can tell how fast your heart is chirapsia by feeling your pulse. Yous can feel your pulse on your wrist or neck. Place the tips of your index and center fingers on the inner wrist of your other arm, but below the base of your pollex. Or, place the tips of your alphabetize and eye fingers on your lower neck, on either side of your windpipe. Press lightly with your fingers until yous feel the claret pulsing below your fingers. You may need to motion your fingers around slightly up or down until y'all feel the pulsing.
You lot can count the number of beats in 10 seconds and multiply past 6 to determine your heart rate in beats per minute. A normal heart rate, at residuum, is fifty to 100 beats per minute.
Your Heart Charge per unit: Pulse in 10 seconds ten half-dozen = _
Learn more than about your pulse and target middle rate.
Heart Rhythms on ECG
The eye'due south electrical organisation triggers the heartbeat. Each shell of the heart is represented on the electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) by a wave arm.
The normal heart rhythm (normal sinus rhythm) shows the electrical activity in the heart is following the normal pathway. The rhythm is regular and the node is normal (about 50 to 100 beats per infinitesimal).
Tachycardia: fast eye rhythm (greater than 100 beats per minute)
Bradycardia: deadening heart rhythm (less than sixty beats per infinitesimal)
The Heart'southward Electric System
The atria (the heart's upper chambers) and ventricles (the middle'due south lower chambers) work together, alternately contracting and relaxing to pump claret through the center. The electric arrangement of the heart is the power source that makes this possible. Here's what happens during a normal heartbeat:
Irregular middle rhythms can also occur in normal, healthy hearts. Arrhythmias can likewise exist caused by certain substances or medications, such every bit caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, cocaine, inhaled aerosols, diet pills, and cough and common cold remedies. Emotional states such equally shock, fearfulness or stress can also cause irregular heart rhythms.
Arrhythmias that are recurrent or related to an underlying centre condition are more than concerning and should always exist evaluated by a doctor.
In about cases, treating the underlying condition volition take intendance of the arrhythmia. If non, many medications and procedures are available to eliminate or control the aberrant center rhythm.
What are the types of arrhythmias?
- Tachycardia: A fast heart rhythm with a rate of more than 100 beats per infinitesimal.
- Bradycardia : A slow eye rhythm with a rate below 60 beats per infinitesimal.
- Supraventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that begin in the atria (the eye's upper chambers). "Supra" means higher up; "ventricular" refers to the lower chambers of the heart, or ventricles.
- Ventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that brainstorm in the ventricles (the heart's lower chambers).
- Bradyarrhythmias: Slow middle rhythms that may be caused by illness in the heart's conduction arrangement, such equally the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node or His-Purkinje network.
Types of Supraventricular Arrhythmias
Supraventricular arrhythmias begin in the atria
Types of supraventricular arrhythmias include:
Premature atrial contractions (PACs)
Early, actress heartbeats that originate in the atria.
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)
A rapid simply regular centre rhythm that comes from the atria. This type of arrhythmia begins and ends of a sudden.
Accessory pathway tachycardias (bypass tract tachycardias)
A fast middle rhythm caused by an extra, aberrant electric pathway or connection between the atria and ventricles. The impulses travel through the extra pathways too equally the usual route. This allows the impulses to travel effectually the heart very quickly, causing the heart to beat out unusually fast (example: Wolff- Parkinson-White syndrome).
AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia (AVNRT)
A fast heart rhythm acquired by the presence of more than one pathway through the atrioventricular (AV) node.
Atrial tachycardia
A rapid centre rhythm that originates in the atria.
Atrial fibrillation
A very common irregular heart rhythm. Many impulses begin and spread through the atria, competing for a chance to travel through the AV node. The resulting rhythm is disorganized, rapid and irregular. Because the impulses are traveling through the atria in a disorderly fashion, there is a loss of coordinated atrial contraction.
- Learn more well-nigh atrial fibrillation.
Atrial flutter
An atrial arrhythmia caused by one or more rapid circuits in the atrium. Atrial flutter is usually more organized and regular than atrial fibrillation.
Types of Ventricular Arrhythmias
A ventricular arrhythmia begins in the heart's ventricles.
Types of ventricular arrhythmias include:
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
Early, actress heartbeats that originate in the ventricles. Nigh of the time, PVCs don't crusade any symptoms or crave treatment. This blazon of arrhythmia is common and can be related to stress, too much caffeine or nicotine, or exercise. They can be as well be caused by heart illness or electrolyte imbalance. People who have several PVCs and/or symptoms associated with them should be evaluated past a cardiologist (center doctor).
- Learn more about premature ventricular contractions.
Ventricular tachycardia (5-tach)
A rapid heartbeat that originates in the ventricles. The rapid rhythm keeps the center from adequately filling with blood, and less blood is able to pump through the body. V-tach can be serious, peculiarly in people with heart disease, and may be associated with more symptoms than other types of arrhythmia. A cardiologist should evaluate this status.
- Larn more about ventricular tachycardia.
Ventricular fibrillation (Five-fib)
An erratic, disorganized firing of impulses from the ventricles. The ventricles quiver and cannot generate an effective contraction, which results in a lack of claret being delivered to the body. This is a medical emergency that must be treated with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation (delivery of an energy shock to the center musculus to restore a normal rhythm) equally soon as possible.
- Acquire more most sudden cardiac death.
Long QT
The QT interval is the expanse on the ECG that represents the time it takes for the center muscle to contract and and then recover, or for the electrical impulse to fire and then recharge. When the QT interval is longer than normal, it increases the chance for "torsade de pointes," a life-threatening course of ventricular tachycardia.
- Learn more than about long QT Syndrome (LQTS)
Types of Bradyarrhythmias
A bradyarrhythmia is a ho-hum heart rhythm that is ordinarily acquired by disease in the heart's conduction system. Types of bradyarrhythmias include:
Sinus node dysfunction
Slow eye rhythms due to an aberrant SA node.
Heart block
A filibuster or complete block of the electrical impulse equally it travels from the sinus node to the ventricles. The level of the block or delay may occur in the AV node or His-Purkinje system. The heartbeat may be irregular and slow.
- Learn more most middle block.
Management and Treatment
How is an arrhythmia treated ?
Treatment depends on the type and severity of your arrhythmia. In some cases, no treatment is necessary. Handling options include medications, lifestyle changes, invasive therapies, electrical devices or surgery.
Medications
Antiarrhythmic drugs are medications used to catechumen the arrhythmia to a normal sinus rhythm or to preclude an arrhythmia. Other medications may include heart rate-control drugs and anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs such every bit warfarin (a "blood thinner") or aspirin, which reduce your risk of stroke or developing blood clots.It is important that you know the names of your medications, why they are prescribed, how oftentimes and at what times to take them, what side furnishings may occur, and what medications yous have previously taken for your arrhythmia.
- Common Medications for Arrythmias
Lifestyle changes
Arrhythmias may be related to certain lifestyle factors. The following tips tin aid limit the occurrence of arrhythmias:
- If yous smoke, stop.
- Limit your intake of alcohol.
- Limit or cease using caffeine. Some people are sensitive to caffeine and may detect more symptoms when using caffeinated products, such as tea, java, colas and some over-the- counter medications.
- Avoid using stimulants. Beware of stimulants used in cough and cold medications and herbal or nutritional supplements. Some of these substances contain ingredients that cause irregular heart rhythms. Read the label and enquire your physician or pharmacist which medication is best for you.
- Your family may too want to be involved in your care by learning to recognize your symptoms and how to start CPR if needed.
- If yous observe that your irregular center rhythm occurs more frequently with certain activities, yous should avoid them.
Invasive therapies
Electrical cardioversion and catheter ablation are invasive therapies used to treat or eliminate irregular heart rhythms. Your medico will decide the best treatment for you and hash out the benefits and risks of these therapies with you.
- Electric cardioversion Patients with persistent arrhythmias, such every bit atrial fibrillation, may not be able to attain a normal heart rhythm with drug therapy lonely. Electrical cardioversion delivers an electrical stupor to your chest wall, which synchronizes the centre and allows the normal rhythm to restart. This procedure is done subsequently you receive short-acting anesthesia.
- Catheter ablation : During ablation, energy is delivered through a catheter to tiny areas of the heart muscle. This energy can either "disconnect" the pathway of the aberrant rhythm, block the aberrant pulses and promote normal conduction of impulses, or disconnect the electrical pathway between the atria and the ventricles.
- Pulmonary vein isolation: In patients with frequent, paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation, isolation of the pulmonary veins is a procedure that uses special catheters to render bands of vein tissue, thought to cause atrial fibrillation, dysfunctional. The goal is to isolate, rather than ablate, the foci responsible for triggering atrial fibrillation through a circumferential conduction cake.
- Electrical devices
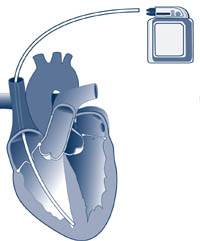
- Permanent pacemaker : A device that sends pocket-sized electric impulses to the eye muscle to maintain a normal center rate. The pacemaker has a pulse generator (which houses a battery and a tiny computer) and leads (wires) that send impulses from the pulse generator to your heart muscle, too every bit sense the centre's electrical activeness. Pacemakers are generally used to forbid the center from beating too slowly. Newer pacemakers have many sophisticated features that are designed to aid manage arrhythmias, optimize heart rate-related functions and ameliorate synchronization.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) : A sophisticated electronic device used primarily to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation — two life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms. The ICD constantly monitors the heart rhythm. When it detects a very fast, aberrant middle rhythm, it delivers free energy to the heart muscle to cause the heart to beat in a normal rhythm once again.
There are several ways an ICD can restore a normal heart rhythm:
- Antitachycardia pacing (ATP): When the middle beats too fast, a series of small electrical impulses are delivered to the heart muscle to restore a normal heart rate and rhythm.
- Cardioversion: A depression-free energy shock is delivered at the same time as the heartbeat to restore a normal eye rhythm.
- Defibrillation: When the heart is beating dangerously fast or irregularly, a college energy daze is delivered to the heart muscle to restore a normal rhythm.
- Antibrachycardia pacing: Many ICDs provide back-up pacing to prevent heart rhythms that are too slow.
Heart surgery
Surgery may be needed to correct arrhythmias that tin can't be controlled with medications or nonsurgical handling methods. Arrhythmia surgery may also be recommended if you need surgery, such as valve surgery or featherbed surgery, to correct other forms of heart disease. The Maze and modified Maze procedures are 2 surgeries used to right atrial fibrillation.Your md will determine the best treatment for y'all and talk over these options with you lot, including more information about surgical treatment if it is an appropriate treatment option.
Resources
Doctors vary in quality due to differences in grooming and experience; hospitals differ in the number of services available. The more than complex your medical problem, the greater these differences in quality get and the more they matter.
Clearly, the medico and hospital that y'all cull for complex, specialized medical intendance volition take a direct bear upon on how well y'all exercise. To aid you make this choice, please review our Miller Family Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Constitute Outcomes.
Cleveland Clinic Eye, Vascular & Thoracic Plant Cardiologists and Surgeons
Choosing a doctor to treat your abnormal heart rhythm depends on where you are in your diagnosis and treatment. The post-obit Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Found Sections and Departments care for patients with Arrhythmias:
- Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing: cardiology evaluation for medical management or electrophysiology procedures or devices - Call Cardiology Appointments at toll-gratuitous 800.223.2273, extension 4-6697 or asking an appointment online.
- Section of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: surgery evaluation for surgical treatment for atrial fibrillation, epicardial lead placement, and in some cases if necessary, lead and device implantation and removal. For more data, please contact us.
- Y'all may also use our MyConsult second opinion consultation using the Net.
The Centre, Vascular & Thoracic Establish has specialized centers to treat certain populations of patients:
- Center for Atrial Fibrillation
- Ventricular Arrhythmia Heart
- Inherited Arrhythmia Clinic
Learn more than about experts who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias.
For younger patients with aberrant heart rhythms:
- Visit The Center for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Diseases web site
- Find a pediatric cardiologist
See Well-nigh Usa to learn more nigh the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family unit Eye, Vascular & Thoracic Found.
Contact
If you need more information, click here to contact u.s.a., chat online with a nurse or call the Miller Family unit Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Plant Resource & Information Nurse at 216.445.9288 or toll-free at 866.289.6911. We would be happy to assist you.
Condign a Patient
- Brand an appointment
- Programme Your Visit
- Billing & Insurance
- Visitor Amenities
Treatment Options
- Arrhythmia Treatments
Treatment Guides
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- All Miller Family Eye, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Handling Guides
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic tests are used to diagnose your abnormal heartbeat and the virtually constructive treatment method.
- Diagnostic testing
- Aberrant Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
- Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
- Brugada Syndrome
- Common Medications for Arrhythmias
- Center Cake
- Eye Palpitations
- Long Q-T Syndrome
- Premature Ventricular Contractions
- Brusk Q-T Syndrome (SQTS)
- Sudden Cardiac Death (Sudden Cardiac Arrest)
- Syncope
- Venricular Tachycardia
- Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW)
Anatomy
- How the heart beats
- Your heart and blood vessels
Webchats
Our webchats and video chats give patients and visitors some other opportunity to ask questions and interact with our physicians.
- Abnormal Center Rhythm webchats and video chats
- All Miller Family Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute webchats
Videos and Podcasts
- Middle Rhythm Disorders and Treatments Videos
- All Miller Family unit Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Found Videos
- Centre and Vascular Disease Podcasts
Interactive Tools
- Miller Family Centre, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Interactive Tools
Resources Links
- Recovery at home
- Support Groups and Data
- Visit Wellness Essentials - Read articles on rhythm disorders and healthy living on Wellness Hub
- Follow Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Found webchats and news stories on Twitter
- Subscribe to Heart, Vascular & Thoracic eNews
Surgical Outcomes
Why cull Cleveland Dispensary for your care?
Our outcomes speak for themselves. Please review our facts and figures and if you have any questions don't hesitate to ask.
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16749-arrhythmia
0 Response to "What to Do to Get Heart Rhythm Normally Again"
Post a Comment